Statement:
If
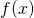 and
and 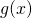 are differentiable on an open interval containing
are differentiable on an open interval containing 
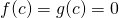
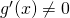 for
for 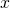 near (but not equal to)
near (but not equal to) 
Then
![]() provided that the limit on the right side of the equations exists.
provided that the limit on the right side of the equations exists.
Proof:
Assume the above conditions. Then,
![]()
Dividing the right-hand expression by ![]() , we get
, we get
![]()
Therefore,
![]() , which is what we sought to prove.
, which is what we sought to prove.
